DeepRare AI Revolutionizes Rare Disease Diagnosis with High Accuracy and Transparent Reasoning
February 18, 2026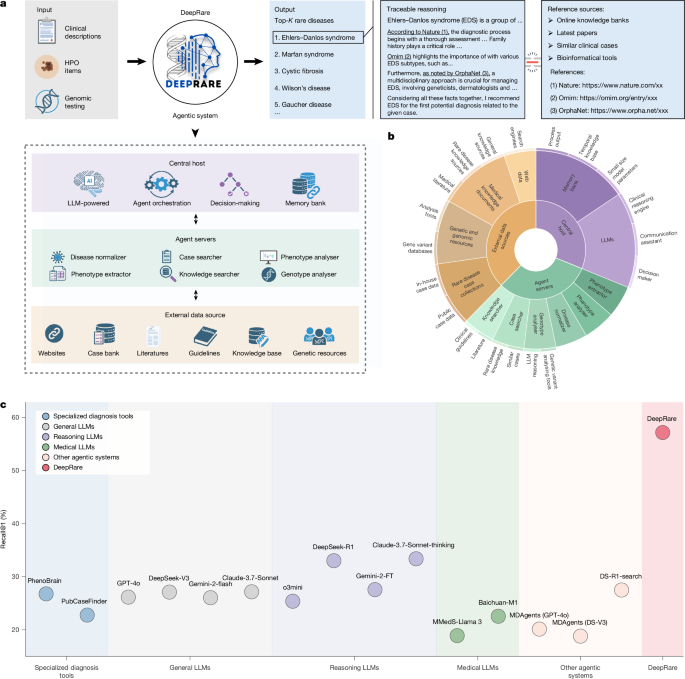
A Nature News & Views article introduces DeepRare, an artificial-intelligence system that assists in diagnosing rare diseases by generating and ranking diagnostic hypotheses and linking each to verifiable medical evidence.
The piece argues that agentic LLM systems like DeepRare offer scalable, interpretable, and accurate support for rare-disease diagnosis, addressing challenges in multidisciplinary knowledge, data scarcity, rapid knowledge updates, and transparent reasoning.
DeepRare combines clinical data, genetic information, and literature searches to propose diagnoses with explicit underlying reasoning, aiming to illuminate the diagnostic process for rare diseases.
In a physician comparison using 163 Xinhua Hospital cases, DeepRare achieved Recall@5 of 78.5% and Recall@1 of 64.4%, outperforming physicians’ averages of 65.6% at Recall@5 and 54.6% at Recall@1.
Evaluation spanned 6,401 clinical cases from nine datasets across Asia, North America, and Europe, including whole-exome sequencing data, covering 2,919 diseases across 14 specialties, with all genetic diagnoses clinically validated.
For especially rare diseases (tail-end, ≤10 cases), DeepRare achieved Recall@1 greater than 0.8 for about one-third of cases, signaling strong generalization to rare conditions.
10 associate chief physicians reviewed 180 cases, validating traceable reasoning chains with an average reference accuracy of 95.4%, highlighting clinical relevance and trustworthy evidence links.
The article notes the traditional diagnostic odyssey faced by roughly 300 million people with rare diseases, who endure long journeys with multiple consultations and misdiagnoses.
DeepRare was deployed as a user-friendly web diagnostic copilot for clinicians, and its robustness was tested across different underlying LLMs and modules, demonstrating the advantage of an agentic, multi-tool architecture over single-model systems.
The system processes heterogeneous inputs—free-text clinical descriptions, structured HPO terms, and genomic data (VCF/WES)—to generate a ranked list of candidate diagnoses with evidence-backed reasoning.
A self-reflective loop within DeepRare re-evaluates hypotheses via additional searches to curb over-diagnosis and LLM hallucinations, iterating until resolution.
Integrating HPO and genetics significantly boosted performance, with Recall@1 rising to 69.1% in Xinhua and 63.6% in Hunan, and outperforming Exomiser across cohorts; multi-modal inputs yielded Recall@1 of 69.1%.
Summary based on 2 sources
Get a daily email with more AI stories
Sources
Nature • Feb 18, 2026
An agentic system for rare disease diagnosis with traceable reasoning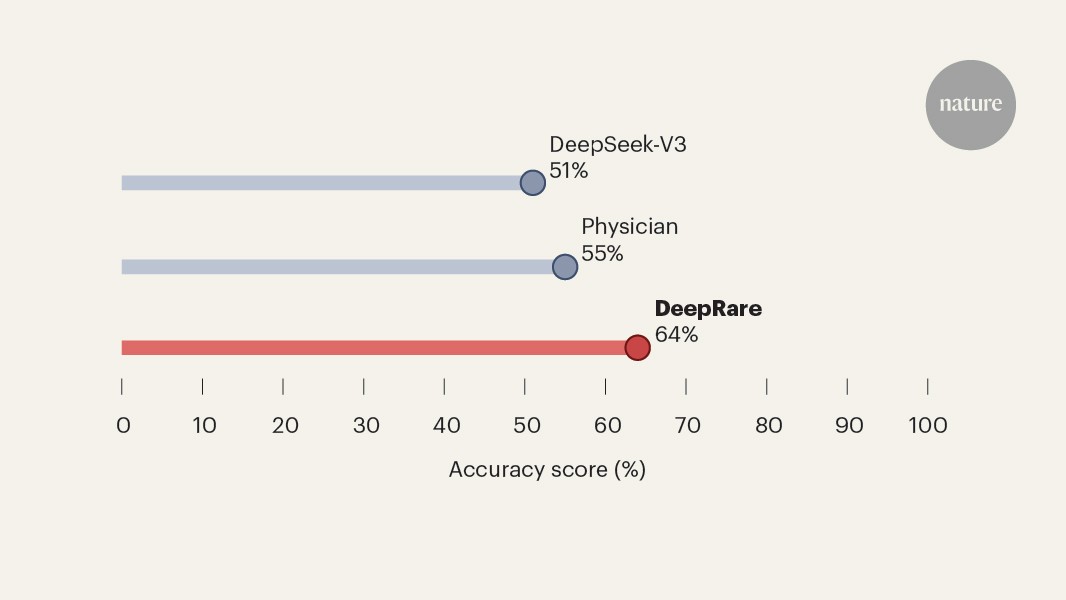
Nature • Feb 18, 2026
AI succeeds in diagnosing rare diseases