Breakthrough Quantum Network Achieves 370 km Secure Communication with Integrated Photonics
February 11, 2026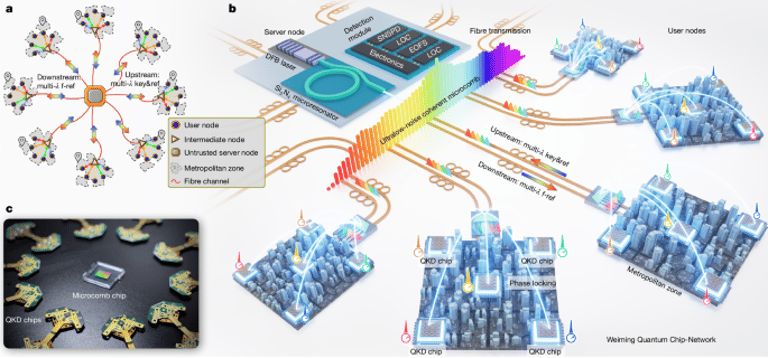
In a network demonstration, the experiment implements SNS-TF-QKD across ten WDM channels linking 20 client chips over distances up to 370 km, achieving a total network capability of NL/2 = 3,700 km, with phase tracking maintained through a dual-λ method to preserve coherence across channels and distances.
The integrated-photonics TF-QKD network shows potential for scalable growth, reduced hardware complexity, and improved resource sharing in large quantum networks, though practical considerations include further integrating server-side devices and ensuring long-term stability in real-world deployments.
A microcomb server node provides an ultralow-noise, Hz-level linewidth source via self-injection locking of a DFB laser to a high-Q Si3N4 microresonator, delivering a broad set of coherent lines for phase reference and wavelength multiplexing across the network.
The work demonstrates extensive integration and reproducibility of low-noise lasers across multiple client chips, scalable microcomb distribution across zones, and outlines a path toward large-scale, cost-effective QKD networks with integrated photonics.
Large-scale quantum communication networks aim to securely connect many clients over long distances, leveraging TF-QKD within an MDI framework to enable scalable, cost-effective networks with high distance reach and large numbers of users.
Key performance metrics include measured QBER in the X-basis for 204 km at roughly 2.87–3.63% and 370 km at roughly 3.50–4.17%, with secure key rates discussed relative to the PLOB bound, and phase tracking remaining effective despite long-distance injection-locked lasers and fiber drift.
Twenty integrated InP QKD client chips integrate lasers, modulators, and attenuators on a single chip; the lasers are injection-locked to microcomb lines to suppress frequency noise, achieving Hz-scale effective linewidths to enable parallel operation across many channels.
The network architecture, named the Weiming Quantum Chip-Network, uses a central server chip with an integrated optical microcomb on a Silicon Nitride platform and 20 InP-based client transmitters, enabling WDM-based, multi-channel key distribution without the need for trusted relays.
Methodology highlights include LF-based dual-λ phase tracking, WDM-based TF-QKD with microcomb lines spaced at 30 GHz (demonstrated in this proof-of-concept), and sequential operation across channels to manage experimental resources while maintaining parallelism.
Summary based on 1 source
Get a daily email with more Science stories
Source

Nature • Feb 11, 2026
Large-scale quantum communication networks with integrated photonics