New Study Uncovers Cholesterol's Role in Lymphedema, Suggests Novel Treatment Approach
February 11, 2026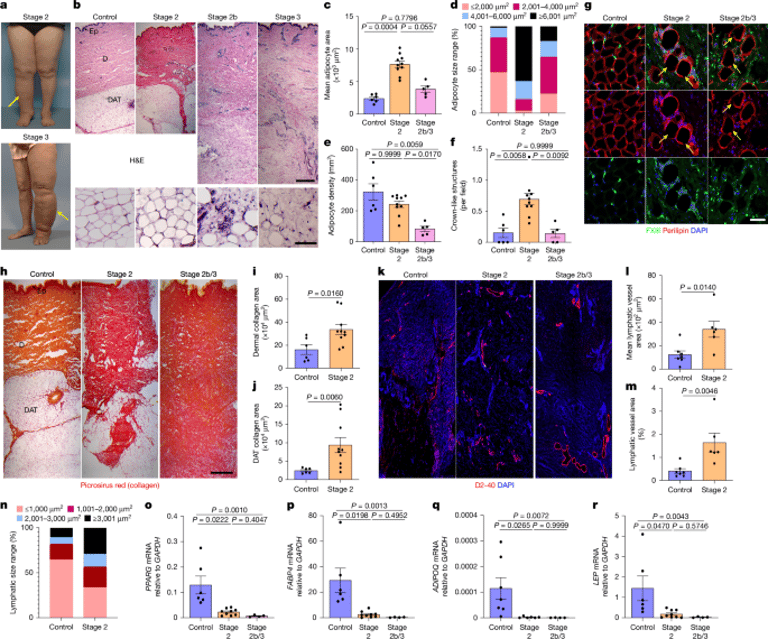
A new study links excessive tissue cholesterol deposition to the pathology of secondary lymphedema, suggesting that how the lymphatic system handles lipids influences disease progression.
The background highlights the lymphatic vasculature’s role in cholesterol transport, adipose tissue remodeling in obesity, and Th2-driven fibrosis and lymphatic dysfunction, with HDL mobilization playing a part in cholesterol homeostasis.
The authors emphasize adipose tissue involvement in lymphedema and propose pharmacologic strategies that remodel adipose tissue and improve cholesterol handling as potential therapies.
The study’s data availability statement notes that multiplex immunoassay, mass spectrometry, and adipokine/cytokine datasets are provided in the supplementary information for independent validation.
By integrating human tissue analyses with mechanistic studies, the work connects cholesterol handling in the lymphatic system to disease outcomes.
A Nature News & Views summary reports that excessive tissue cholesterol is a central feature of the most common type of lymphedema, supported by human samples and mouse model data.
Promoting cholesterol removal from tissues was shown to reduce disease symptoms in the models, pointing to cholesterol clearance as a potential therapeutic strategy.
Summary based on 2 sources
Get a daily email with more Science stories
Sources
Nature • Feb 11, 2026
Targeting excessive cholesterol deposition alleviates secondary lymphoedema
Nature • Feb 11, 2026
Clearing trapped cholesterol could relieve lymphoedema